Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Sewing machines have come a long way since their humble beginnings. Today, they are the backbone of the garment manufacturing industry, significantly increasing productivity, efficiency, and quality. The history of sewing machines in garment manufacturing is a fascinating journey of innovation, technological advancements, and continuous improvement. Over the years, these machines have evolved from simple, manual devices to sophisticated, automated systems that are capable of handling complex tasks in mass production environments.
In this blog post, we will explore the evolution of sewing machines in garment manufacturing. From their origins in the pre-industrial era to the highly advanced, computerized machines used in modern garment factories, we will delve into the historical milestones, technological advancements, and the impact these machines have had on the garment industry.
1. The Early Days: Hand-Sewing to Mechanization
Before the invention of sewing machines, garments were created entirely by hand. This was a labor-intensive process that required skilled workers to stitch together fabric pieces, often taking days to complete a single item. While hand sewing provided some level of precision and flexibility, it was not efficient enough to meet the demands of an expanding garment market.
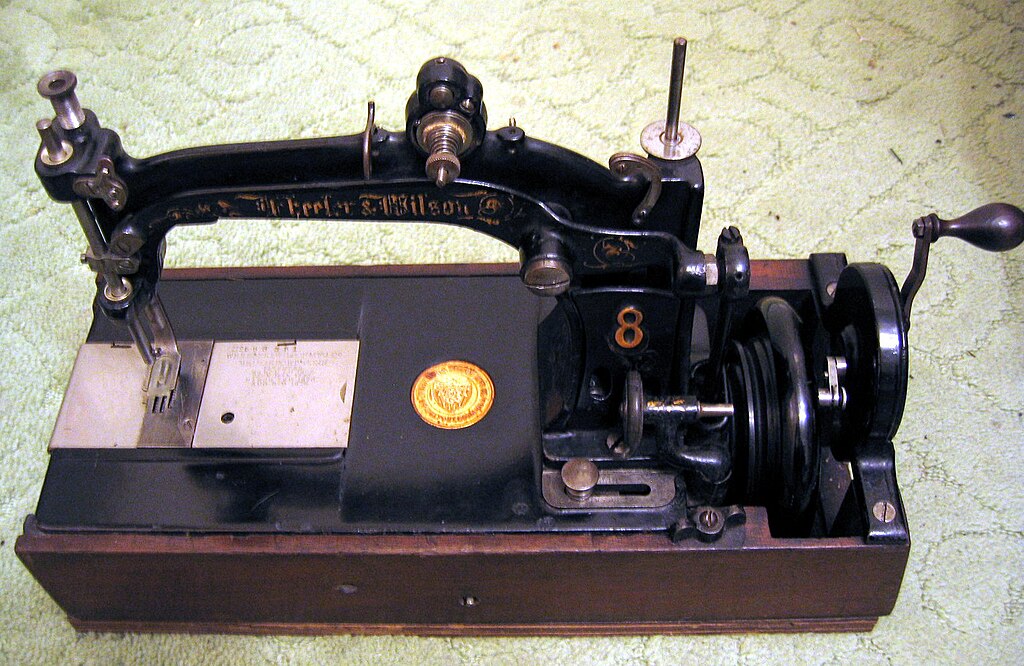
The first breakthrough came in the early 19th century when Elias Howe, an American inventor, patented the first practical sewing machine in 1846. However, it was Isaac Singer, an entrepreneur, who played a pivotal role in the widespread adoption of sewing machines. Singer made significant improvements to Howe’s design and introduced the first mass-produced sewing machine.
The design of the first sewing machine was revolutionary. It featured a needle with an eye near the point, which allowed the machine to sew a lockstitch – a crucial advancement that provided durability and strength to the seams. Singer’s machines quickly became popular for their speed and efficiency, cutting down sewing time dramatically. This laid the foundation for the industrial revolution in garment manufacturing.
The mechanization of sewing processes enabled garment manufacturers to move from small-scale, handcrafted production to large-scale, machine-driven manufacturing. This shift allowed for faster production, lower costs, and the ability to produce garments in bulk. The early days of the sewing machine were a turning point in the garment industry, setting the stage for future innovations.
2. The Rise of Industrial Sewing Machines in the 20th Century
By the early 20th century, the garment manufacturing industry had grown significantly, and there was a clear need for specialized sewing machines that could handle various aspects of garment production. The industrial revolution had already introduced assembly lines for mass production, and sewing machines had to keep up with the demand for faster, more efficient production methods.
During this time, industrial sewing machines began to emerge. These machines were specifically designed for high-volume production environments and featured improvements that made them more efficient and capable of handling a wide range of fabrics.
In the early 1900s, companies like Pfaff and Brother began to introduce machines tailored to specific tasks. For example, the introduction of overlock sewing machines allowed manufacturers to trim and finish fabric edges, preventing fraying and ensuring durability. These machines were essential for high-volume production, particularly in the creation of garments with intricate finishes like shirts, pants, and jackets.
Additionally, machines capable of performing multi-needle stitching and twin-needle stitching were introduced to accommodate the production of garments requiring complex stitching techniques. Industrial sewing machines were faster, more accurate, and more reliable than ever before, further increasing the speed of production and quality of the final products.
The introduction of automatic thread trimmers and bobbin winders in the 1920s eliminated the need for manual intervention during certain stages of the sewing process, allowing for continuous operation. These improvements further increased productivity and reduced human error in the production process, making it easier for manufacturers to meet the growing demand for garments.
The rise of industrial sewing machines in the 20th century marked a turning point in garment manufacturing. The development of specialized machines for various tasks, along with improvements in speed and efficiency, made it possible for manufacturers to produce garments on an industrial scale, revolutionizing the industry.
3. The Advent of Automated and Computerized Sewing Machines
The 1970s and 1980s saw the introduction of automated sewing machines that incorporated advanced technologies such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) and digital interfaces. These machines were capable of performing more complex tasks with greater accuracy and consistency than ever before.
One of the most significant advancements was the introduction of computerized sewing machines. These machines were able to store stitching patterns and automatically adjust settings to create different designs. This technology allowed garment manufacturers to produce intricate and customized designs with ease, providing a level of precision that was previously unattainable.
As computers became more advanced, they began to play a larger role in garment manufacturing. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) systems were introduced to assist with pattern making, allowing designers to create digital patterns that could be easily manipulated and adjusted. This reduced the time spent on manual pattern drafting and allowed manufacturers to make changes to designs quickly and efficiently.
In addition to pattern-making, computerized sewing machines also allowed for more intricate stitch designs, including embroidery stitching. These machines could produce detailed designs with a level of precision that would have been impossible with manual sewing. This opened up new possibilities in garment customization and decoration, leading to the rise of personalized and branded apparel.
Robotic automation also made its way into garment manufacturing in the 1980s. Robots were introduced to assist with tasks such as fabric handling, stitching, and finishing, reducing the need for manual labor and further improving efficiency. The introduction of robotics in the sewing process led to a new era of high-speed, high-precision manufacturing, which continued to evolve in the following decades.
4. Key Types of Modern Sewing Machines in the Industry
Modern garment manufacturing relies on a wide range of specialized sewing machines, each designed for a specific purpose. These machines have significantly improved the quality, speed, and versatility of garment production. Some of the most common types of sewing machines used in the industry today include:
- Overlock Machines (Serger): Overlock machines, also known as sergers, are used to sew over the edge of fabric to prevent fraying. These machines can trim the fabric while simultaneously stitching it, making them essential for garments that require neat, finished edges. Overlock machines are widely used in the production of knitwear, t-shirts, and other garments with stretchy fabrics.
- Flatlock Machines: These machines are used to create flat seams that are often seen in sportswear and activewear. Flatlock stitching eliminates bulky seams, making garments more comfortable and suitable for high-performance activities. These machines are essential in the production of garments designed for fitness, outdoor activities, and active lifestyles.
- Embroidery Machines: Embroidery machines are used to add decorative elements to garments, such as logos, monograms, and intricate designs. These machines use automated stitching techniques to create detailed patterns on fabric, offering a high level of customization and branding potential for manufacturers.
- Buttonhole Machines: These machines are specifically designed to create buttonholes in garments. They can create various types of buttonholes, from simple, single-hole designs to more complex, multi-hole patterns. Buttonhole machines significantly speed up the process of garment assembly, ensuring precise and consistent results.
- Specialized Machines: Some garments, such as jeans or leather jackets, require specialized sewing machines to handle the unique challenges posed by thick or heavy fabrics. Machines designed for these purposes often feature powerful motors, thicker needles, and additional features that allow them to handle heavy-duty materials without compromising stitching quality.
Each of these machines plays a crucial role in garment manufacturing, helping manufacturers achieve the high standards of quality, consistency, and speed that modern consumers demand.
5. The Role of Robotics and AI in Modern Sewing Machines
The most recent advancements in sewing machine technology involve the integration of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) into the manufacturing process. Robotic sewing machines can handle multiple tasks, such as fabric manipulation, stitching, and even quality inspection. These machines offer unparalleled precision and speed, reducing human error and the need for manual labor.
AI-powered machines can predict fabric behavior, optimize stitching paths, and adjust machine settings in real-time. This ability to analyze and respond to fabric characteristics has revolutionized the way garments are manufactured. AI also allows for continuous monitoring of production, ensuring that any issues are detected and addressed immediately, minimizing defects and maximizing efficiency.
Robotic and AI-powered machines have not only increased the speed of garment production but have also made it possible for manufacturers to produce garments with greater customization and complexity. As AI and robotics continue to evolve, the future of garment manufacturing promises even greater advancements in automation and precision.
6. The Impact of Sewing Machine Evolution on the Garment Industry
The evolution of sewing machines has had a profound impact on the garment manufacturing industry. Machines have not only increased production speed but have also improved quality, consistency, and the ability to handle more complex garment designs. These advancements have made it possible for manufacturers to meet the growing demand for fast fashion and custom garments.
The introduction of automated sewing machines has led to a reduction in labor costs, allowing manufacturers to produce garments at a fraction of the cost compared to manual labor. Additionally, the precision and consistency offered by modern machines have resulted in fewer defects, reducing the need for costly rework and returns.
Furthermore, advancements in sustainable sewing technologies have allowed manufacturers to reduce fabric waste and energy consumption. Some machines are now capable of cutting fabric with minimal waste, contributing to more sustainable production practices.
7. Looking Ahead: The Future of Sewing Machines in Garment Manufacturing
As technology continues to advance, the future of sewing machines in garment manufacturing looks promising. 3D knitting machines, which produce seamless garments with minimal fabric waste, are poised to revolutionize the industry. These machines use computerized technology to create garments directly from yarn, eliminating the need for sewing altogether.
In addition to 3D knitting, fully automated garment factories that rely on robotic sewing machines are becoming more feasible. These factories will be able to produce high-quality garments with minimal human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and production time.
Sustainability will also continue to be a major focus in the future of garment manufacturing. Machines that reduce energy consumption, minimize fabric waste, and use eco-friendly materials will become more prevalent as manufacturers strive to meet environmental goals and consumer demand for sustainable products.
Conclusion
The evolution of sewing machines has been a driving force behind the growth and transformation of the garment manufacturing industry. From the early days of hand sewing to the advanced, automated machines of today, sewing technology has played a pivotal role in improving efficiency, quality, and sustainability in garment production. As we look to the future, the continued integration of robotics, AI, and sustainable practices promises to reshape the industry even further, offering exciting opportunities for manufacturers and consumers alike.
The story of sewing machines is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. As technology continues to evolve, it’s clear that the garment manufacturing industry will keep pushing boundaries, creating garments faster, more efficiently, and with greater precision than ever before.
Call to Action:
What do you think about the evolution of sewing machines in the garment industry? How do you see technology shaping the future of garment production? Share your thoughts in the comments below!